This product was successfully added to cart!
品牌商品推荐
更多 >>商品详情
客户评价
| 描述 |
匹罗卡品是一种选择性M3型毒蕈碱乙酰胆碱受体(M3毒蕈碱受体)激动剂。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 |
|
| 靶点 |
M3 muscarinic receptor[1]
|
| 体外研究 |
为了评价匹罗卡品的细胞毒性,分别用光学显微镜和MTT法检测人角膜基质细胞(HCS)的形态和活性。形态学观察表明,暴露于浓度为0.625至20 g/L毛果芸香碱的HCS细胞表现出剂量和时间依赖性增殖迟缓和形态学异常,如细胞收缩、细胞质空泡化、脱离培养基质,最终死亡,而暴露于浓度低于0.625g/L的匹罗卡品组与对照组之间没有观察到明显差异。MTT试验结果表明,毛果芸香碱浓度高于0.625g/L时,HCS细胞的细胞活力随时间和浓度的增加而降低(P<0.01或0.05),而毛果芸香碱浓度低于0.625 g/L的HCS细胞与对照组相比无显著差异[2]。部分毒蕈碱激动剂匹罗卡品在用苯乙肾上腺素(10至200 nM)收缩的大鼠尾动脉孤立段中引起浓度依赖性舒张,EC50为2.4 mM[3]。 |
| 体内研究 |
研究了匹罗卡品诱导的对照大鼠(CN)和运动大鼠(EX)的唾液分泌。毛果芸香碱在EX大鼠中诱导的唾液量显著高于CN大鼠(P<0.01)。相反,EX大鼠唾液中的钠离子浓度显著低于CN大鼠(P<0.05)[1]。 |
| 细胞实验 |
MTT法测定细胞活力。简而言之,将HCS细胞接种到密度为1×104个细胞/100?L/孔的96孔培养板(Nunc)中,并进行培养和处理。每隔4h,将含有毛果芸香碱(0.625至20 g/L)的培养基完全替换为含有1.0 g/L MTT的100?L无血清DMEM/F12培养基,并将细胞在37°C的黑暗中培养4h。小心丢弃含MTT的培养基后,添加150?L二甲基亚砜以在37°C下在黑暗中溶解产生的福尔马赞晶体15分钟,并使用Multiskan GO微孔板读取器测量490 nm处的吸光度[2]。 |
| 动物实验 |
大鼠[1]将10周龄雄性Wistar大鼠分为两组,运动组(EX,n=6)和对照组(CN,n=5)。前大鼠被关在带有滚轮(SN-451)的笼子里40天,允许它们进行自愿运动,而CN大鼠被锁在带有滚轮的笼子里。在第40天,毛果芸香碱诱导的唾液测量如下。简单地说,将大鼠麻醉,将预先称重的棉花置于舌下,并腹腔注射匹罗卡品(0.5 mg/kg)以诱导唾液分泌。然后每10分钟更换一个棉球,持续1小时。再次称量收集的棉球,并通过从最终重量中减去初始重量来计算分泌的唾液质量。 |
| 存储 |
请将产品存放在分析证书中的建议条件下。
|
| 运输 |
室温 |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 密度 | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 431.8±18.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 分子式 | C11H16N2O2 |
| 分子量 | 208.257 |
| 闪点 | 215.0±21.2 °C |
| 精确质量 | 208.121185 |
| PSA | 44.12000 |
| LogP | -0.09 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.585 |
|
匹罗卡品毒性英文版
|
| 符号 |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 |
Danger |
| 危害声明 |
H300 + H330 |
| 警示性声明 |
P260-P264-P284-P301 + P310-P310 |
| 危害码 (欧洲) |
T+: Very toxic; |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) |
26/28 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) |
25-45 |
| 危险品运输编码 | UN 1544 |
| 包装等级 | III |
| 危险类别 | 6.1(b) |
|
Function of inhibitory micronetworks is spared by Na+ channel-acting anticonvulsant drugs. J. Neurosci. 34(29) , 9720-35, (2014)
The mechanisms of action of many CNS drugs have been studied extensively on the level of their target proteins, but the effects of these compounds on the level of complex CNS networks that are compose…
|
|
|
Impairment of GABA release in the hippocampus at the time of the first spontaneous seizure in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 257 , 39-49, (2014)
The alterations in GABA release have not yet been systematically measured along the natural course of temporal lobe epilepsy. In this work, we analyzed GABA extracellular concentrations (using in vivo…
|
|
|
Dynamics of hippocampal acetylcholine release during lithium-pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in rats. J. Neurochem. 131(1) , 42-52, (2014)
The lithium-pilocarpine model is a rat model of epilepsy that mimics status epilepticus in humans. Here, we report changes of acetylcholine (ACh) release in the hippocampus before, during and after st…
|
|
|
ocusertp20 |
|
PILOCARPINE |
|
pilokarpol |
|
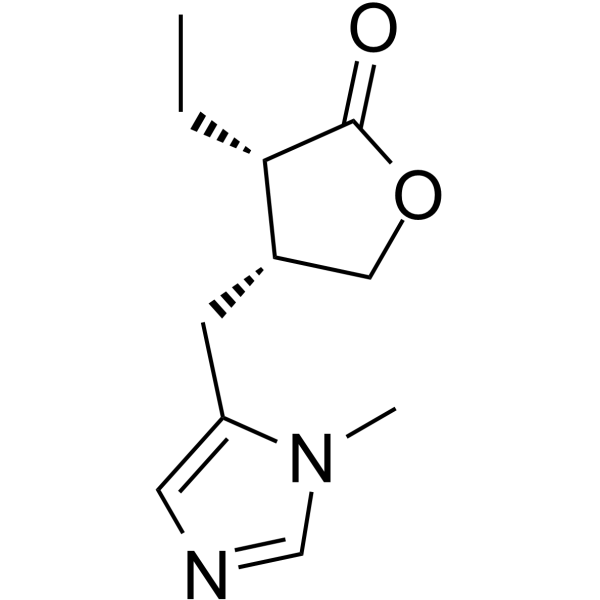
3-ethyl-4-((1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)dihydro-2(3H)-furanone |
|
Pilocarpol |
|
2(3H)-Furanone, 3-ethyldihydro-4-[(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]- |
|
EINECS 202-128-4 |
|
3-Ethyl-4-[(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]dihydro-2(3H)-furanone |
|
Pilocarpin |
|
Syncarpine |
|
Pilokarpin |
|
Ocucarpine |
|
Ocusert |
|
MFCD00153042 |
|
actone |











![3-ethyl-dihydro-4-[(1-methyl-1H-2-mercaptoimidazol-5-yl)methyl]-2(3H)-furanone结构式](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/005/858221-10-0.png)
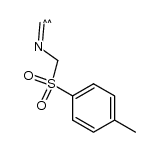
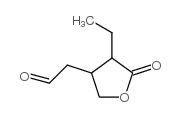
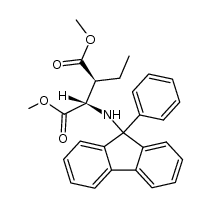
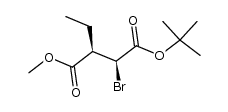
![Butanedioic acid, 2-bromo-3-ethyl-, 4-methyl ester, [S-(R*,S*)]- (9CI)结构式](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/373/146499-97-0.png)